If TRUE, make a notched box plot Notches are used to compare groups;A box and whiskers plot (in the style of Tukey) Source R/geomboxplotr, R/statboxplotr geom_boxplotRd The boxplot compactly displays the distribution of a continuous variable It visualises five summary statistics (the median, two hinges and two whiskers), and all "outlying" points individually geom_boxplot ( mapping = NULL , data Key ggplot2 R functions This section presents the key ggplot2 R function for changing a plot color Set ggplot color manually scale_fill_manual() for box plot, bar plot, violin plot, dot plot, etc scale_color_manual() or scale_colour_manual() for lines and points Use colorbrewer palettes

Quick R Boxplots
R boxplot color transparent
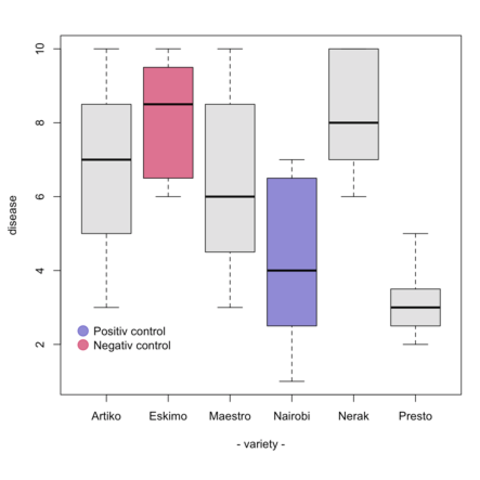
R boxplot color transparent-If the notches of two boxes do not overlap, this suggests that the medians are significantly differentA boxplot summarizes the distribution of a numeric variable for one or several groups It can be usefull to add colors to specific groups to highlight them For exemple, positive and negative controls are likely to be in different colors The easiest way is to give a vector (myColor here) of colors when you call the boxplot() function




How To Color Boxplots By A Variable In R With Ggplot2 Data Viz With Python And R
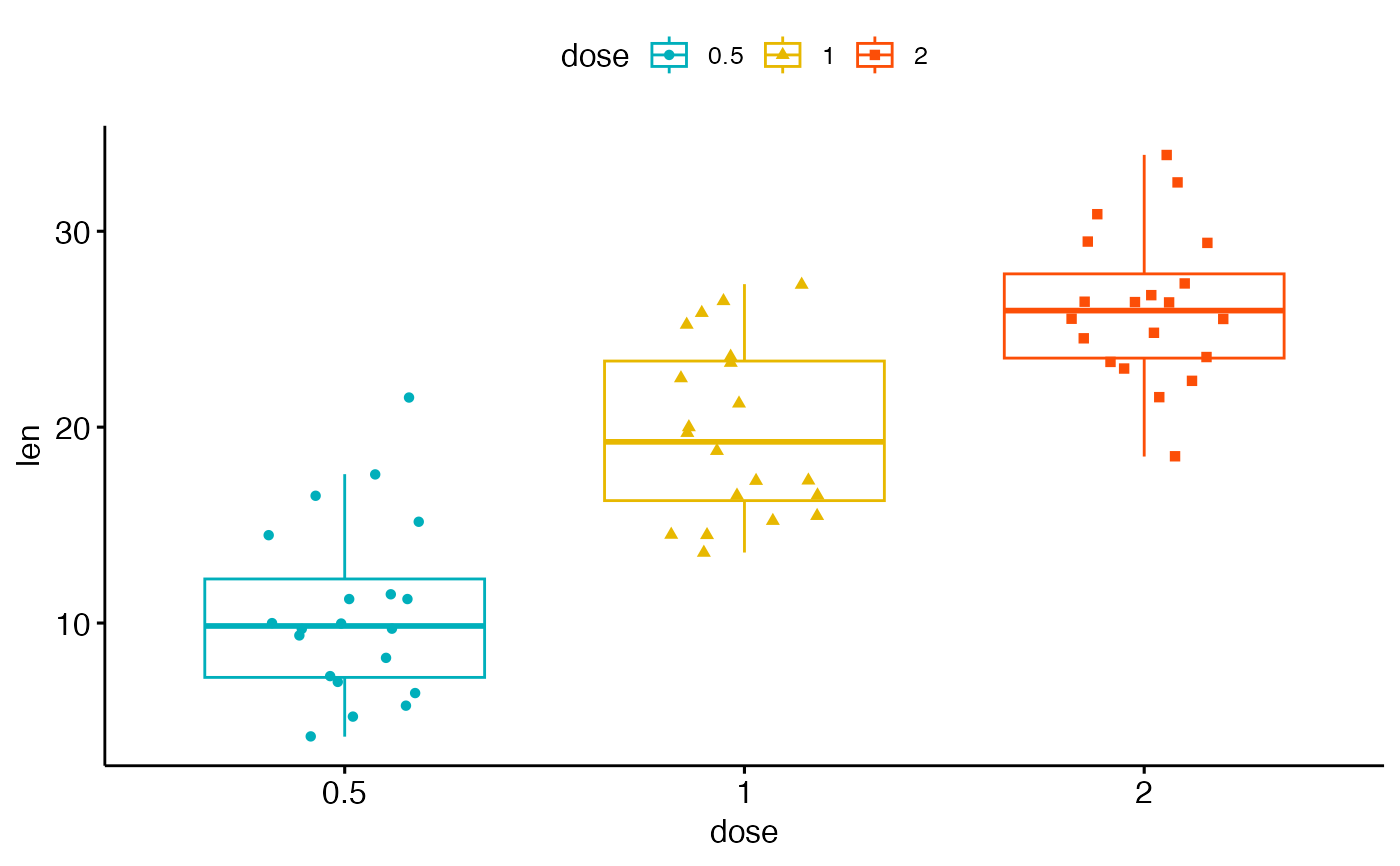
Fill the boxplot with color 1) Default For filling the boxplot with your choice of color then you can use the fill attribute command to add colors inside the geom_boxplot() function The fill will be under geom_boxplot( ) as it is variable in this caseDefault colors The following R code changes the color of the graph by the levels of dose # Box plot bpggplot(ToothGrowth, aes(x=dose, y=len, fill=dose)) geom_boxplot() bp # Scatter plot spggplot(mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg, color=cyl)) geom_point() sp Box plots with custom fill colors ¶ This plot illustrates how to create two types of box plots (rectangular and notched), and how to fill them with custom colors by accessing the properties of the artists of the box plots Additionally, the labels parameter is used to provide xtick labels for each sample A good general reference on
Or you can type colors() in R Studio console to get the list of colours available in R Box Plot when Variables are Categorical Often times, you have categorical columns in your data set ggplot2 generates aesthetically appealing box plots for categorical variables too R boxplot with data points and outliers in a different color Here is ggplot2 based code to do that I also used package ggrepel and function geom_text_repel to deal with data labels Oftentimes we want to make a plot which plots the colors according to some categorical variable I will be showing two ways which you can do this Method 1 can be rather tedious if you have many categories, but is a straightforward method if you are new to R and want to understand better what's going on
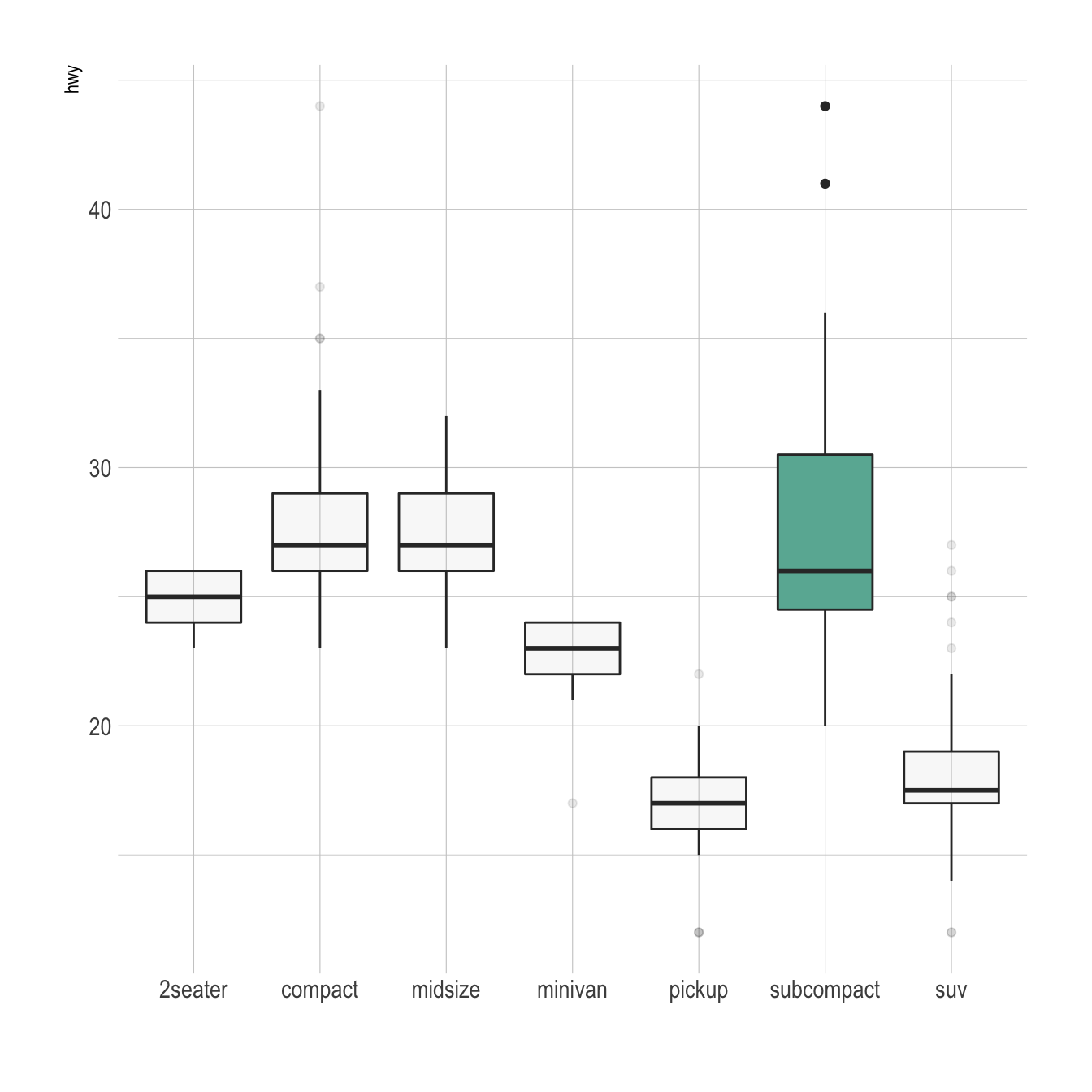
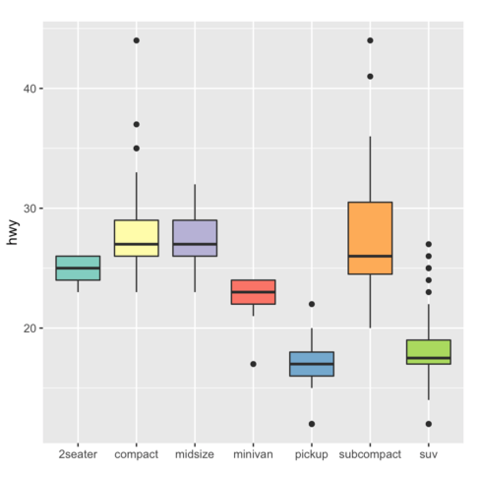
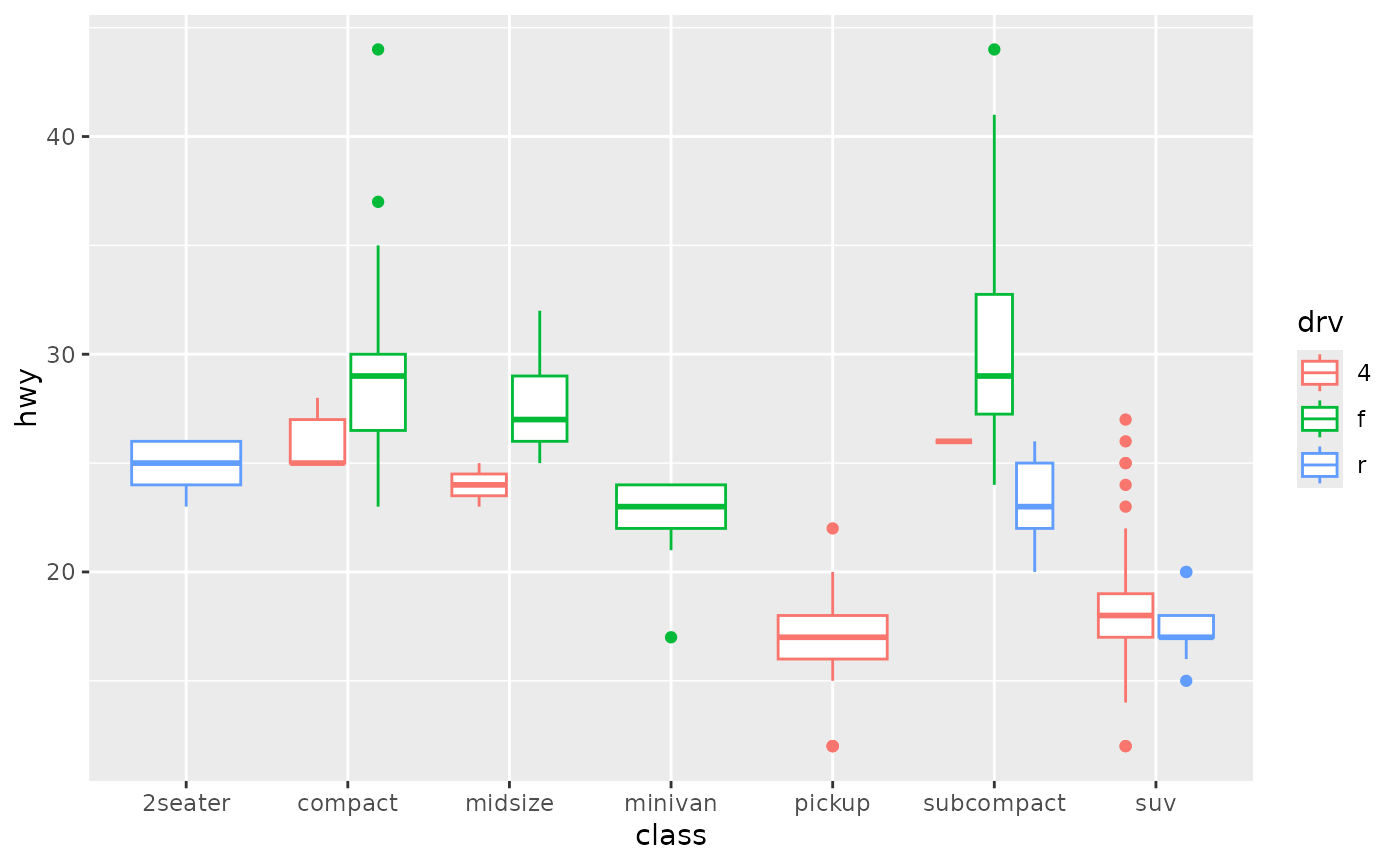
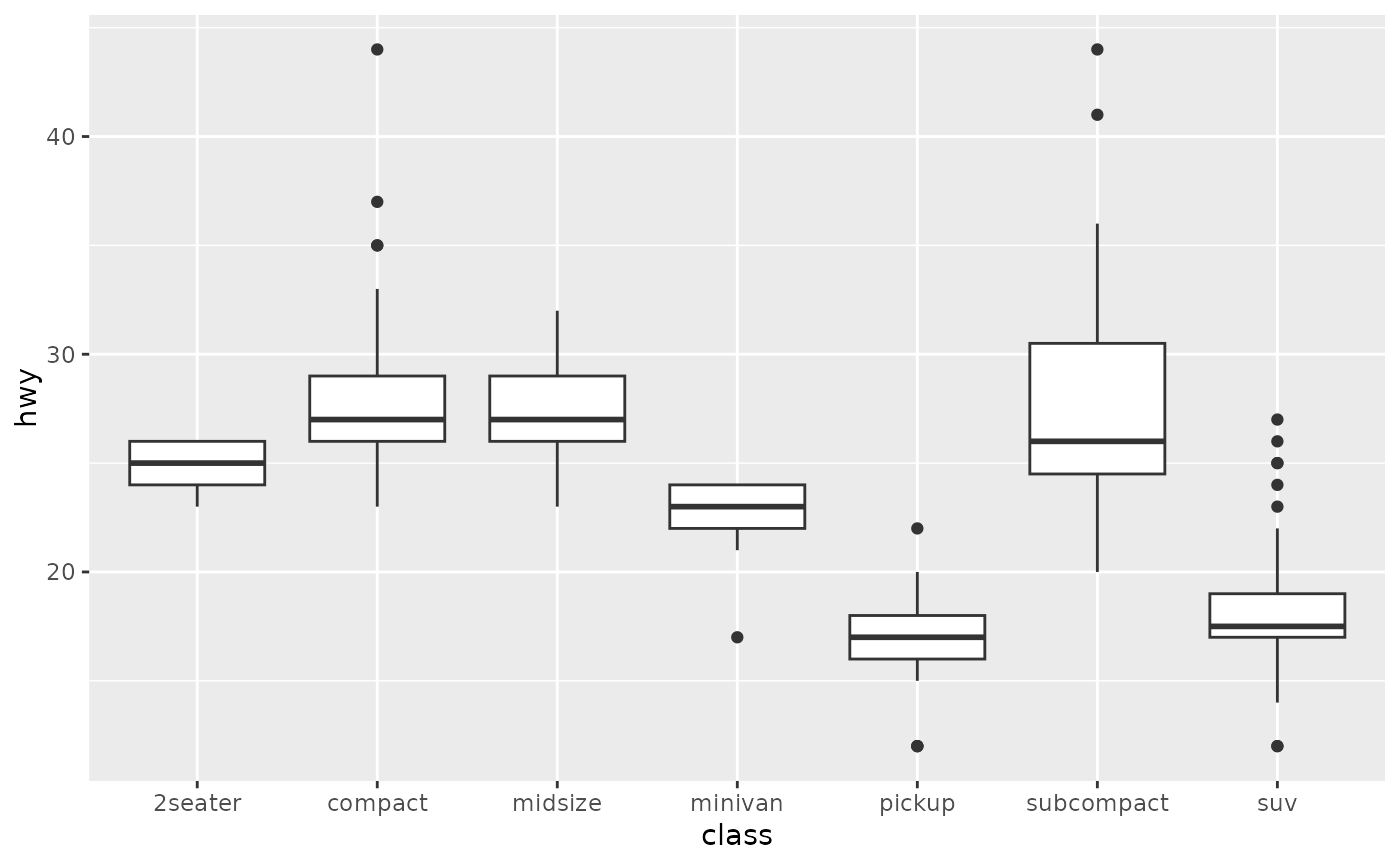
# library library (ggplot2) # The mtcars dataset is natively available in R #head(mpg) # Top Left Set a unique color with fill, colour, and alpha ggplot (mpg, aes (x= class, y= hwy)) geom_boxplot (color= "red", fill= "orange", alpha= 02) # Top Right Set a different color for each group ggplot (mpg, aes (x= class, y= hwy, fill= class)) geom_boxplot (alpha= 03) theme Look at ?boxplot to find that there's an argument border= that does what you want For example For example boxplot(count ~ spray, data = InsectSprays, col = "lightgray", border=c("blue", "green", "blue", "green", "blue", "green"))Key R functions Key R function geom_boxplot() ggplot2 package Key arguments to customize the plot width the width of the box plot;




How To Color Box And Whisker Plot Yatomizonor




Boxplot In R Boxplot By Group Multiple Box Plot
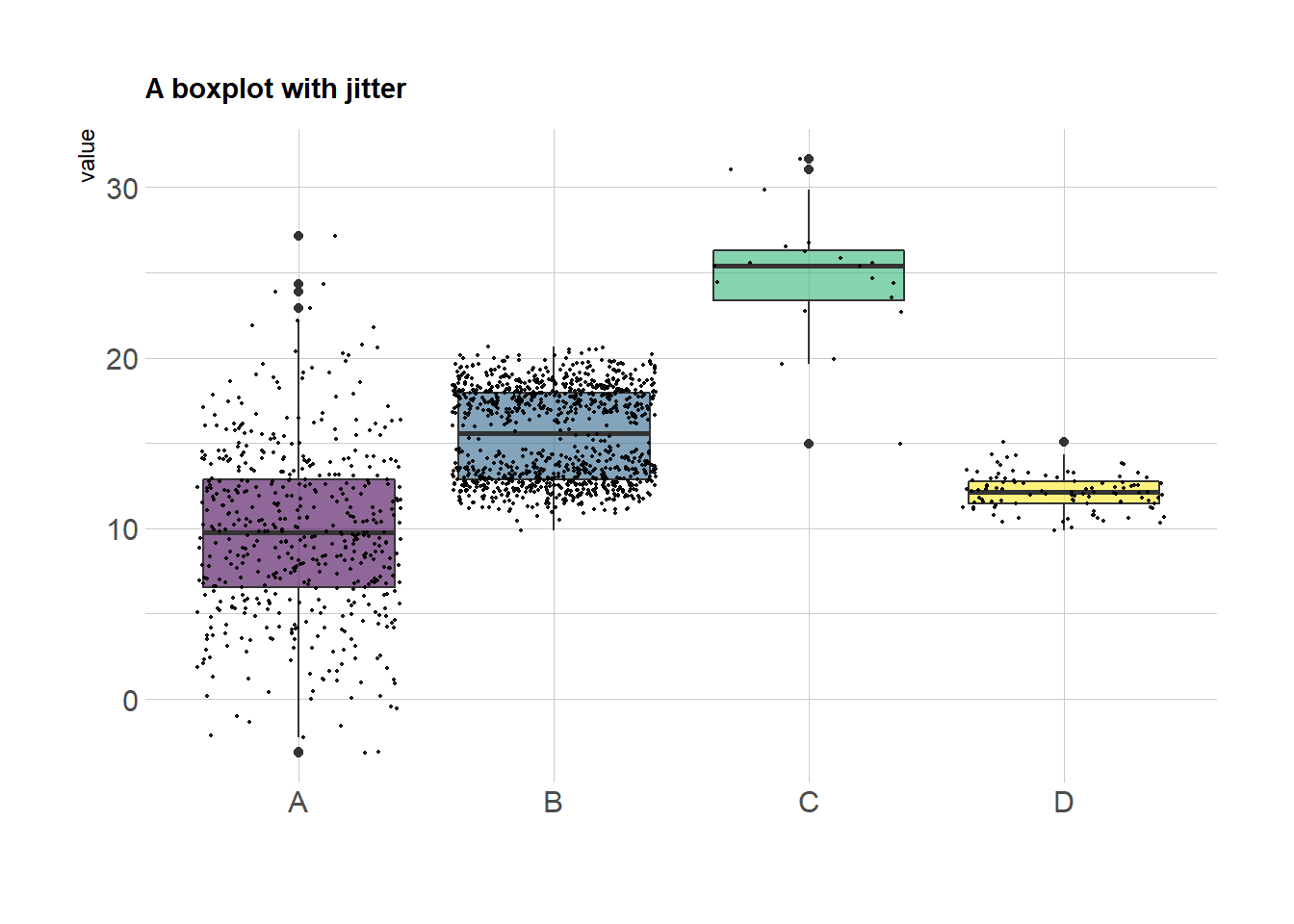
Adding jittered points (a stripchart) to a box plot in ggplot is useful to see the underlying distribution of the data You will need to use geom_jitter A good practice is removing the outliers of the box plot with outliershape = NA, as the jitter will add them again Recall that you can flip the axes with coord_flip or flipping the variablesBoxplot(len~supp*dose, data=ToothGrowth, notch=TRUE, col=(c("gold","darkgreen")), main="Tooth Growth", xlab="Suppliment and Dose") click to view In the notched boxplot, if two boxes' notches do not overlap this is 'strong evidence' their medians differ (Chambers et al, 19, p 62) Colors recycle In the example above, if I had listed 6 colors, each box would have itsAn optional vector of colors for the outlines of the boxplots The values in border are recycled if the length of border is less than the number of plots col if col is nonnull it is assumed to contain colors to be used to colour the bodies of the box plots




Boxplot With Respect To Two Factors Using Ggplot2 In R Cross Validated



Ggplot2 Box Plot Quick Start Guide R Software And Data Visualization Easy Guides Wiki Sthda
Boxplots with Specific Colors Boxplots with actual data points are one of the best ways to visualize the distribution of multiple variables at the same time Creating a beautiful plot with Boxplots in Python Pandas is very easy In an earlier post, we saw a good example of how to create publication quality boxplots with Pandas and Seaborn If The box plot is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on the five number summary minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum Box plots are useful for detecting outliers and for comparing distributions It shows the shape, central tendancy and variability of the dataA box plot is a good way to get an overall picture of the data set in a compact manner Create a BoxWhisker Plot To get started, you need a set of data to work with By default, box plot use a white color for the boxes You can change this with the fill argument # Change the colors of individual boxes (default fill colors) ggplot




Help Online Tutorials Box Plot



Control Ggplot2 Boxplot Colors The R Graph Gallery
Boxplot(len ~ dose, data = ToothGrowth, frame = FALSE, names = c("D05", "D1", "D2")) Change color # Change the color of border using one single color boxplot(len ~ dose, data = ToothGrowth, frame = FALSE, border = "steelblue") # Change the color of border # Add Color to R ggplot boxplot # Importing the ggplot2 library library(ggplot2) # Create a Boxplot ggplot(diamonds, aes(x = cut, y = price, fill = cut)) geom_boxplot(outliercolour="black", outliershape=16, outliersize=2) Change Outliners of R ggplot2 BoxplotOf course you can easily apply an uniform color to every boxes Find a list of the numerous colors you can use here The most common ones are b blue g



Box Plot Ggboxplot Ggpubr



3
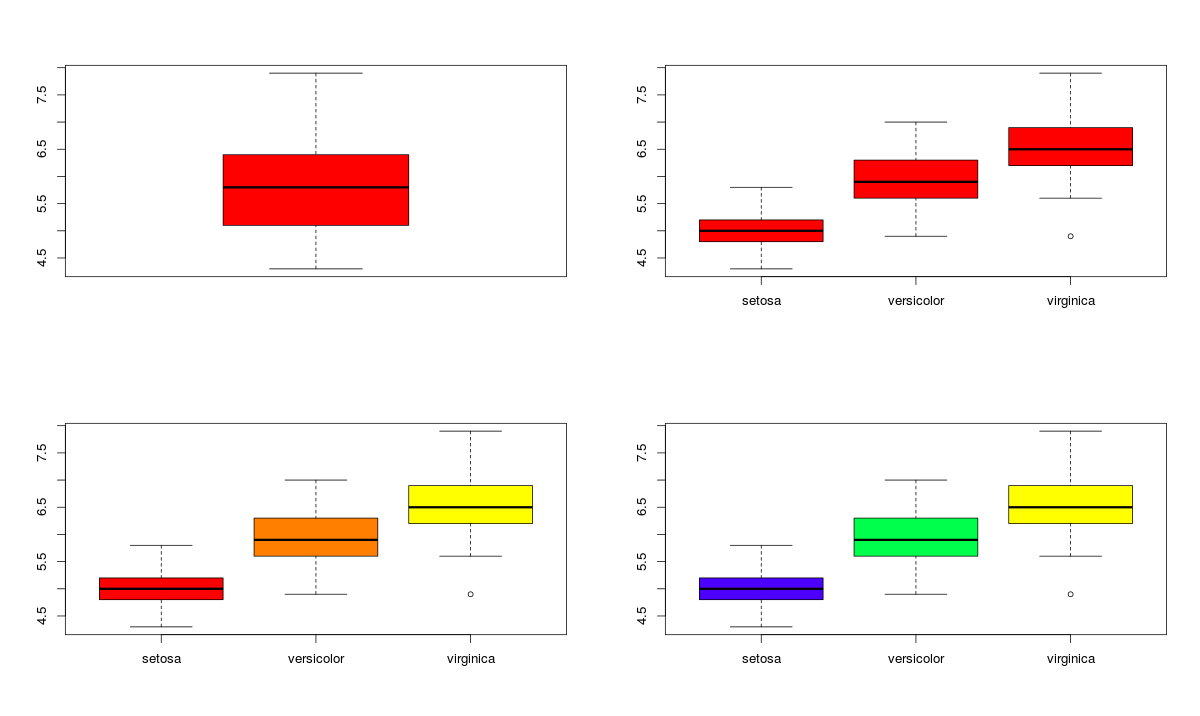
This R tutorial describes how to create a box plot using R software and ggplot2 package The function geom_boxplot () is used A simplified format is geom_boxplot(outliercolour="black", outliershape=16 , outliersize=2, notch=FALSE)The most basic graphics function in R is the plot function This function has multiple arguments to configure the final plot add a title, change axes labels, customize colors, or change line types, among others In this tutorial you will learn how to plot in R and how to fully customize the resulting plot 1 Plot function in R library(ggplot2) ch < ggplot(chickwts,aes(x=feed,y=weight,color=feed)) geom_boxplot(outliercolor="black") ch Output Same fill Here, we will use the keyword fill Since we need the same color in the fill of boxplots, we will write the command inside the geom_boxplot ( ) By default, fill for outliers is black



Chapter 2 Distributions R Gallery Book



Matplotlib Boxplot A Helpful Illustrated Guide Finxter
Box plot color by group The boxplot function contains an argument named col where you can specify a vector of colors of the same length of the number of groups See colors or palettes to choose your colors or the palette generator to create your own palettesColouring different group data in boxplot using r The Boxplot in the link, I want to display different background colour for example 04 in one group, 0507 in another group while from 0011 in another group All groups could be displayed on different background colour with description of legend or notes at bottom on graphs how to fill boxes in Boxplot with different colors Follow 725 views (last 30 days) Show older comments Poulomi Ganguli on Vote 2 ⋮



Boxplot The R Graph Gallery



Boxplots Ggplot Applied R Code
Adding color to Plotly plots by Dr Juan H Klopper Last updated almost 3 years ago Hide Comments (–) Hide Toolbars × Post on Twitter Facebook Google # Change Colors of a R ggplot Violin plot # Importing the ggplot2 library library(ggplot2) # Create a Violin plot ggplot(diamonds, aes(x = cut, y = price)) geom_violin(fill = "seagreen") scale_y_log10() Change Colors of an R ggplot2 Violin Plot using Columns This R ggplot violin plot example, we show how to change the violin plot colors using column dataNotch logicalIf TRUE, creates a notched boxplotThe notch displays a confidence interval around the median which is normally based on the median / 158*IQR/sqrt(n)Notches are used to compare groups;



1




How To Change Ggplot2 Boxplot Color With Points Stack Overflow
Boxplot(ozone, ozone_norm, temp, temp_norm, main = "Multiple boxplots for comparision", at = c(1,2,4,5), names = c("ozone", "normal", "temp", "normal"), las = 2, col = c("orange","red"), border = "brown", horizontal = TRUE, notch = TRUE )If the notches of two boxes do not overlap, this suggests that the medians are significantly different Notches are used to compare groups;6 Boxplots Boxplots encode the five number summary of a numeric variable, and provide a decent way to compare many numeric distributions The visual task of comparing multiple boxplots is relatively easy (ie, compare position along a common scale) compared to some common alternatives (eg, a trellis display of histograms, like 51), but the boxplot is sometimes
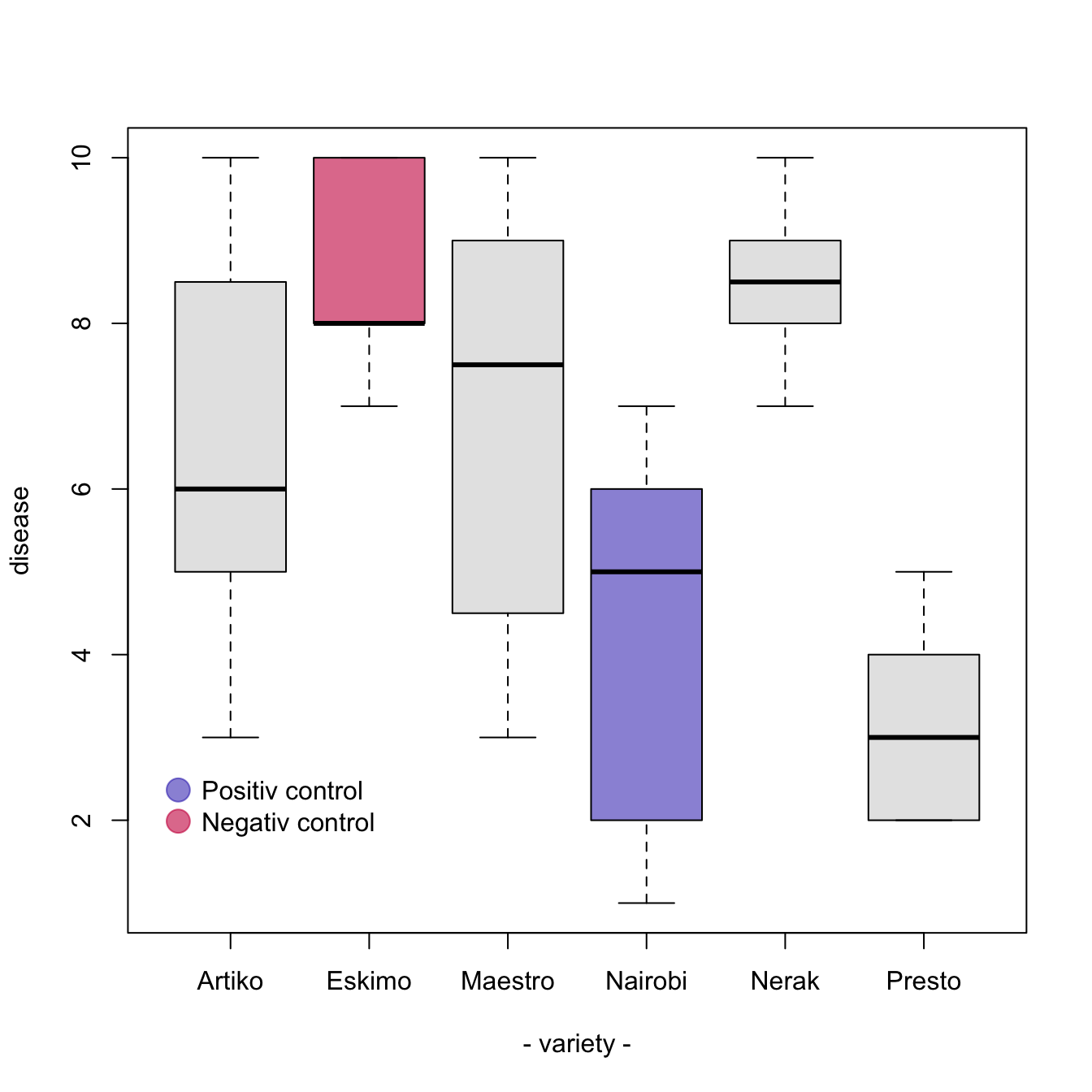



Add Color To Specific Groups Of A Boxplot The R Graph Gallery




Chapter 11 Boxplots And Bar Graphs
103 Color Utilities in R R has a number of utilities for dealing with colors and color palettes in your plots For starters, the grDevices package has two functions colorRamp Take a palette of colors and return a function that takes valeus between 0 and 1, indicating the extremes of the color palette (eg see the gray() function) colorRampPalette Take a palette of colors and return aIn order to solve this issue, you can add points to boxplot in R with the stripchart function (jittered data points will avoid to overplot the outliers) as follows stripchart(x, method = "jitter", pch = 19, add = TRUE, col = "blue") Since R 400 boxplots are gray by default instead of white scale_fill_brewer () function is useful when you want to use color palette from RColorBrewer and fill boxplots with colors color palette Here we have used Orange and Red color palette using 'palette="OrRd"' inside scale_fill_brewer () Check out this post to learn more about the available color palettes in RColorBrewer




Quick R Boxplots



Ggplot2 Box Plot Quick Start Guide R Software And Data Visualization Easy Guides Wiki Sthda
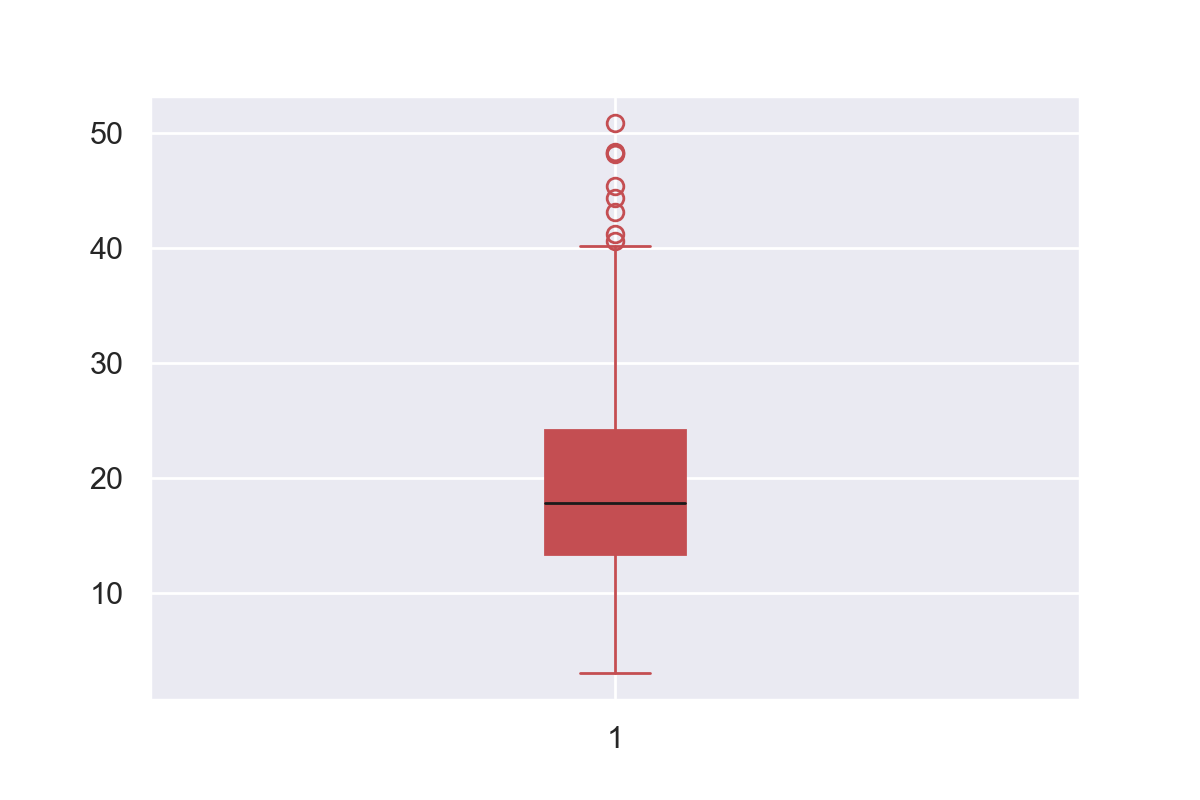
the body of the boxplot consists of a "box" (hence, the name), which goes from the first quartile (Q1) to the third quartile (Q3) within the box, a vertical line is drawn at the Q2, the median of the data set two horizontal lines, called whiskers, extend from the front and back of the box the front whisker goes from Q1 to the smallest nonBoxplot label size where 10 is normal size characters If zero labels will not be added xaxt Plotting parameter for xaxis generation Default is not to produce an xaxis horizontal If true draw boxplots horizontally the default is false, produce vertical box plots lwd Width(s) of lines in box plots col Color(s) of bplots01 02 03 04 05 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 New Label for Hours New Label for Counts New Legend Title New label for A Single Boxplot Modified Color 5 DoubleBoxplot 51



Box Plots R Base Graphs Easy Guides Wiki Sthda
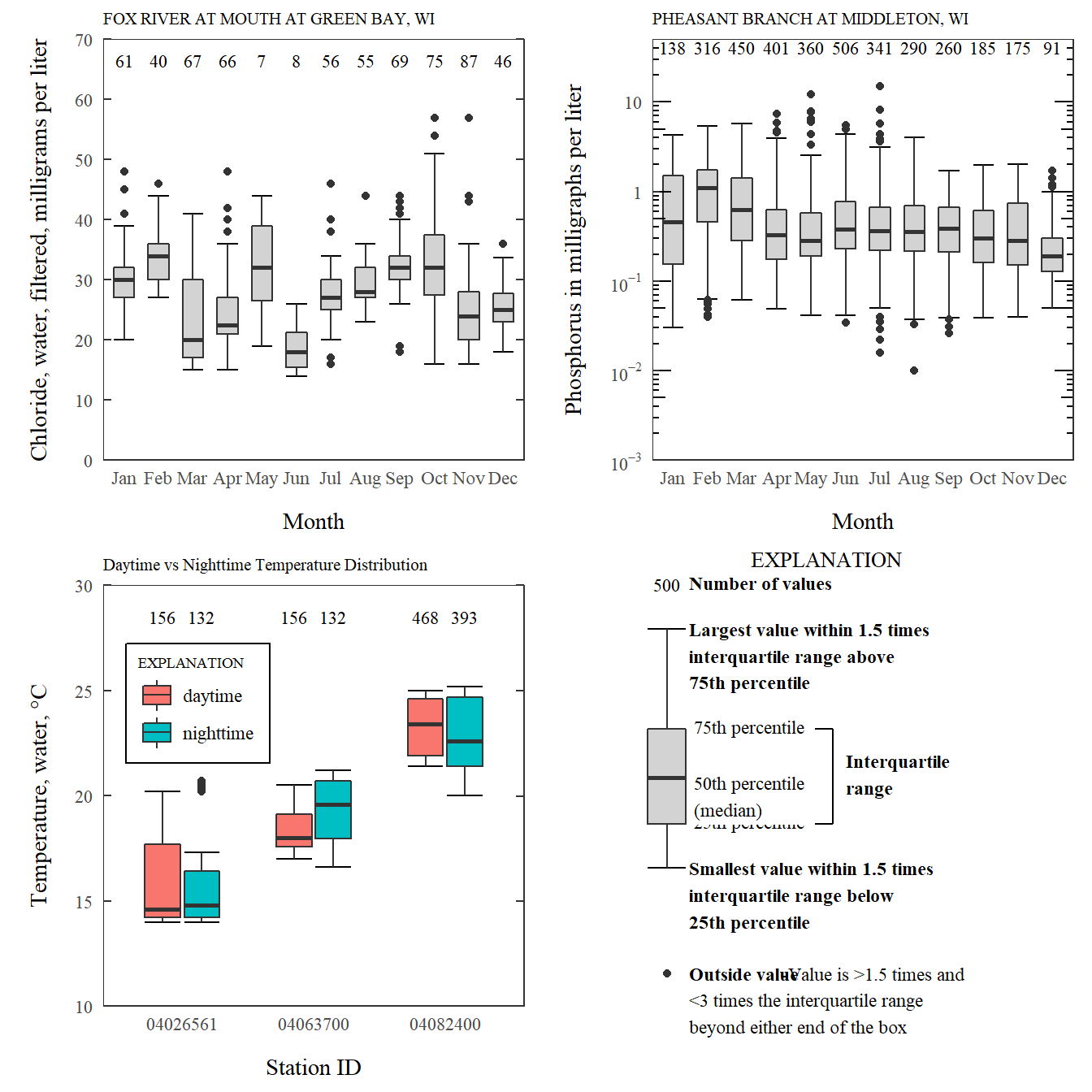



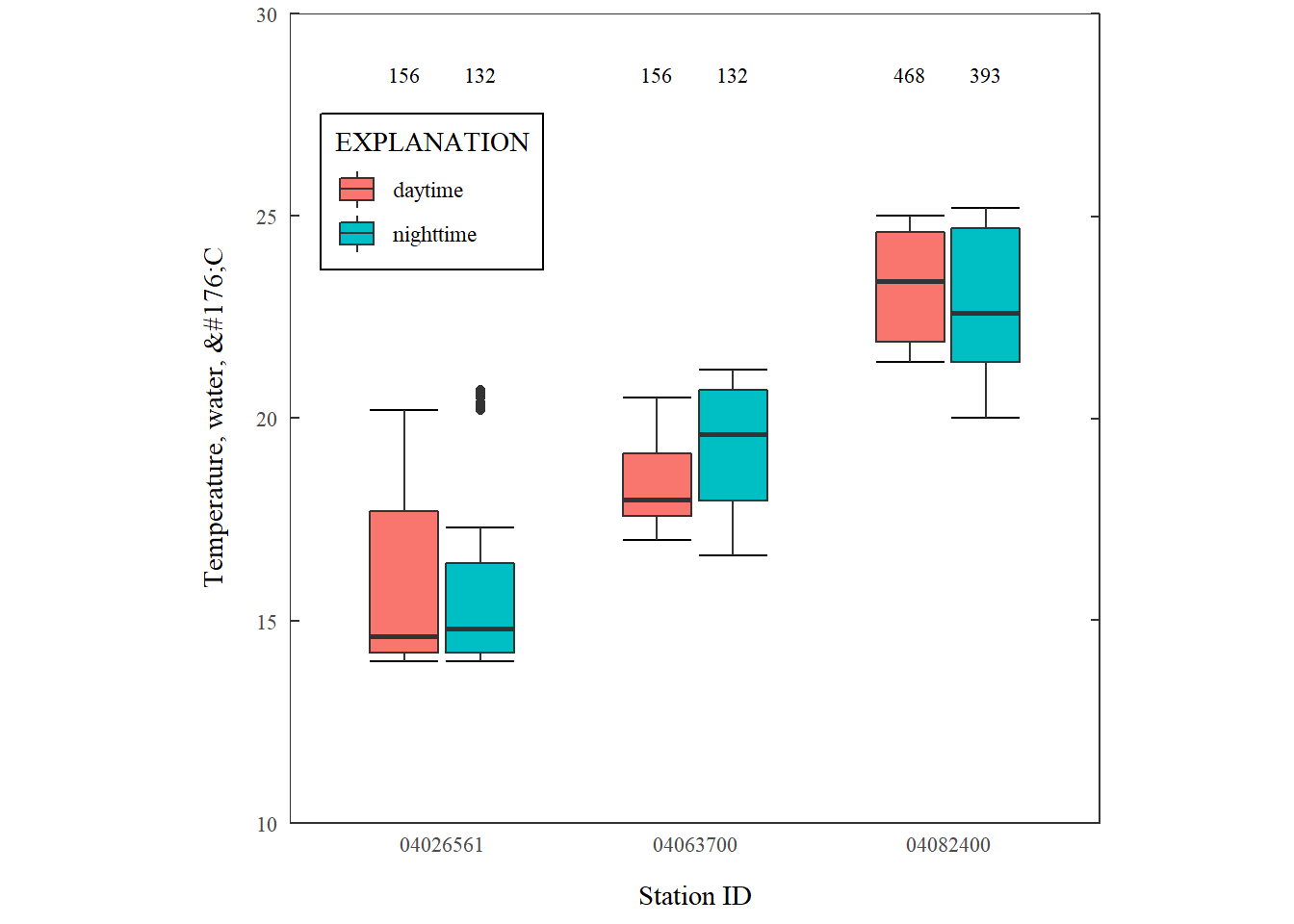
Exploring Ggplot2 Boxplots Defining Limits And Adjusting Style Water Data For The Nation Blog
ChartBoxplot( R, names = TRUE, asTufte = FALSE, plotengine = "default", sortby = c(NULL, "mean", "median", "variance"), colorset = "black", symbolcolor = "red", meansymbol = 1, mediansymbol = "", outliersymbol = 1, showdata = NULL, addmean = TRUE, sortascending = FALSE, xlab = "Return", main = "Return Distribution Comparison", elementcolor = "darkgray", This article presents the top R color palettes for changing the default color of a graph generated using either the ggplot2 package or the R base plot functions You'll learn how to use the top 6 predefined color palettes in R, available in different R packages Viridis color scales viridis packageColorbrewer palettes RColorBrewer packageGrey color palettes ggplot2If the notches of two boxes do not



Change Color Of Ggplot2 Boxplot In R 3 Examples Set Col Fill In Plot




R Box Whisker Plot Ggplot2 Learn By Example
R Boxplots Boxplots are a measure of how well distributed is the data in a data set It divides the data set into three quartiles This graph represents the minimum, maximum, median, first quartile and third quartile in the data set It is also useful in comparing the distribution of data across data sets by drawing boxplots for each of them You can use the geometric object geom_boxplot() from ggplot2 library to draw a boxplot() in R Boxplots() in R helps to visualize the distribution of the data by quartile and detect the presence of outliers We will use the airquality dataset to introduce boxplot() in R with ggplot Here the boxes in boxplot will be empty We can color a boxplot like this using color argument inside aesthetics function aes() as shown below df %>% ggplot(aes(x=age_group, y=height, color=age_group)) geom_boxplot(width=05,lwd=1) labs(subtitle="Coloring Boxplot with Colors by a Variable")




Boxplot In R How To Make Boxplots Learn With Example




R Box Whisker Plot Ggplot2 Learn By Example
Using Hex Values as Colors Instead of using a color name, color can also be defined with a hexadecimal value We define a color as a 6 hexadecimal digit number of the form #RRGGBBWhere the RR is for red, GG for green and BB for blue and value ranges from 00 to FF For example, #FF0000 would be red and #00FF00 would be green similarly, #FFFFFF would be white andBox Plots in R How to make an interactive box plot in R Examples of box plots in R that are grouped, colored, and display the underlying data distribution This page in another language




How To Color Box And Whisker Plot Yatomizonor




Chapter 11 Boxplots And Bar Graphs




Quick R Boxplots




Change Color Of Ggplot2 Boxplot In R Geeksforgeeks




Boss Of All Plots Box Plots R Bloggers




Ggplot2 Aes Group Overrides Default Grouping R Census




How To Color Box And Whisker Plot Yatomizonor




How To Change The Boundary Color Of Boxplot Stack Overflow




How To Specify Colors To Boxplots In Seaborn Python And R Tips




The Boxplot Function In R R Charts




R Boxplot To Create Box Plot With Numerous Examples
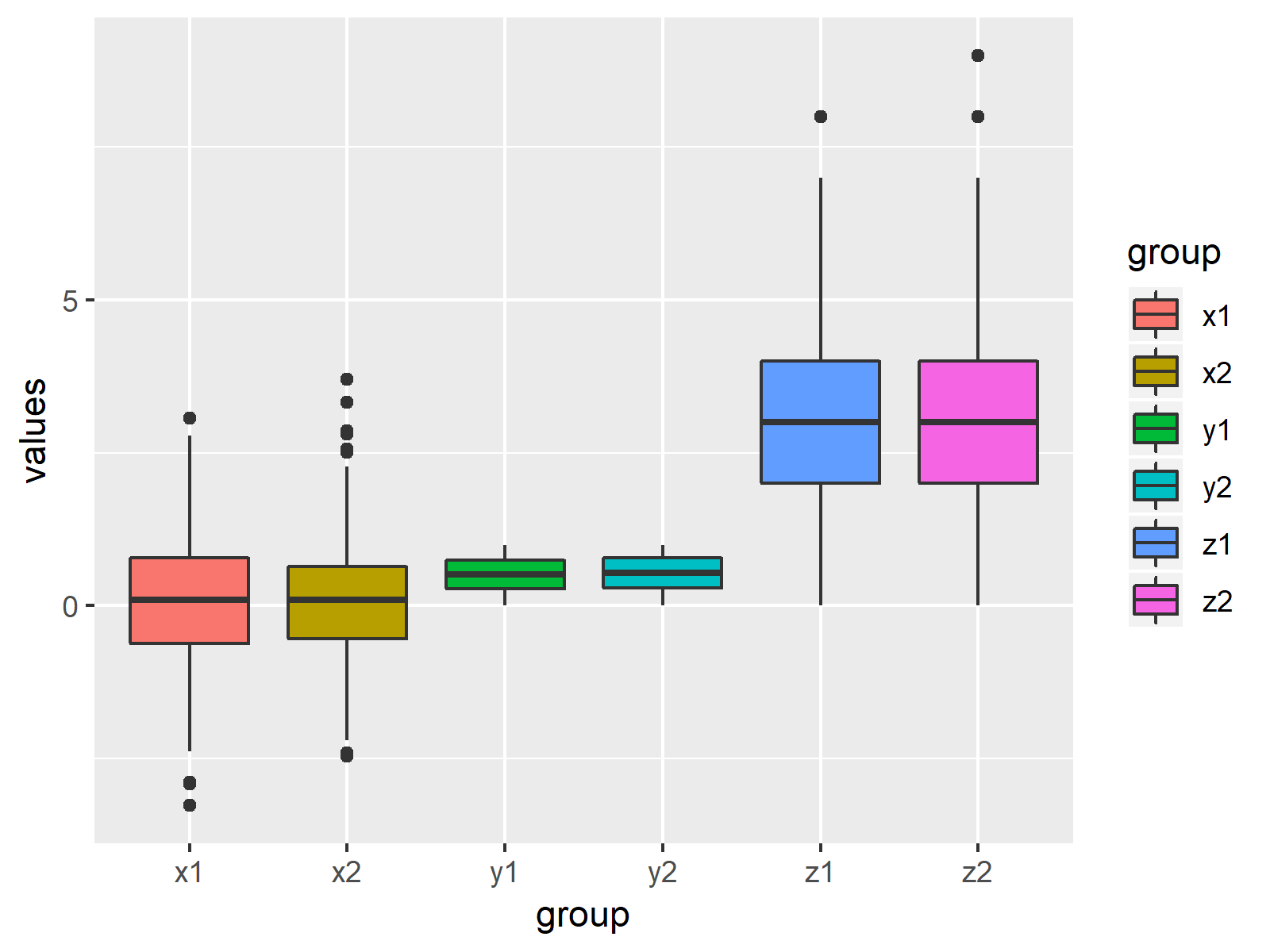



Boxplot In R 9 Examples Create A Box And Whisker Plot In Rstudio




Box Plot By Group In R R Charts
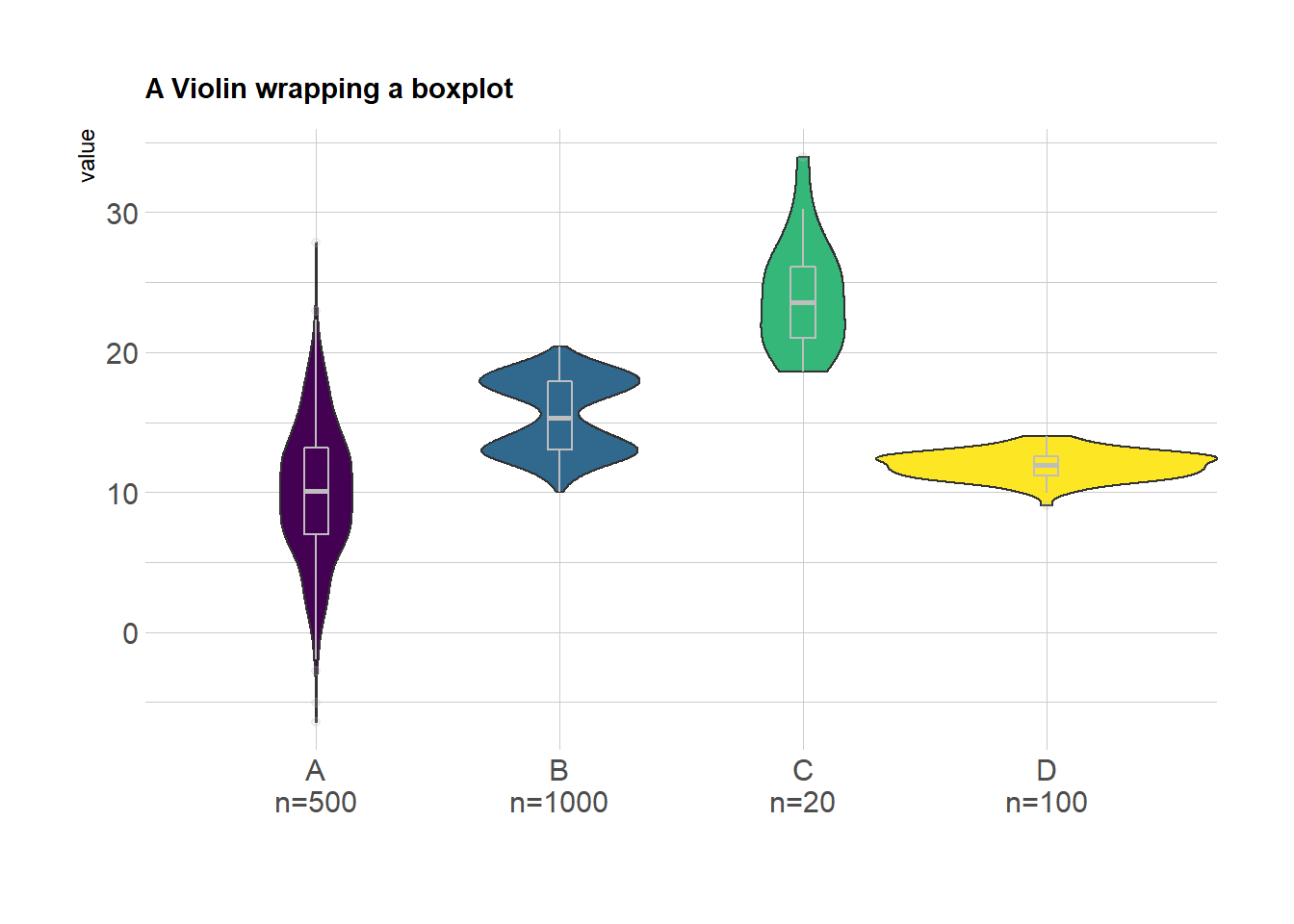



Chapter 2 Distributions R Gallery Book




Creating Plots In R Using Ggplot2 Part 10 Boxplots



Beautiful Minimalist Boxplots With R And Ggplot2 Biochemistry Resources




Box Plot In Ggplot2 R Charts
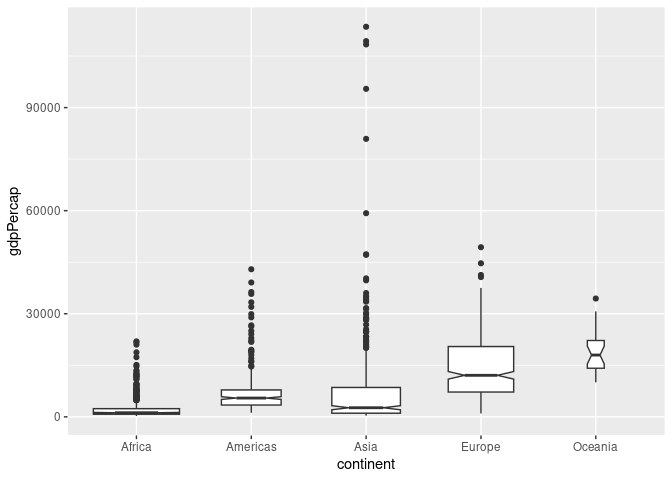



Box Plots And Relations




R Boxplot To Create Box Plot With Numerous Examples
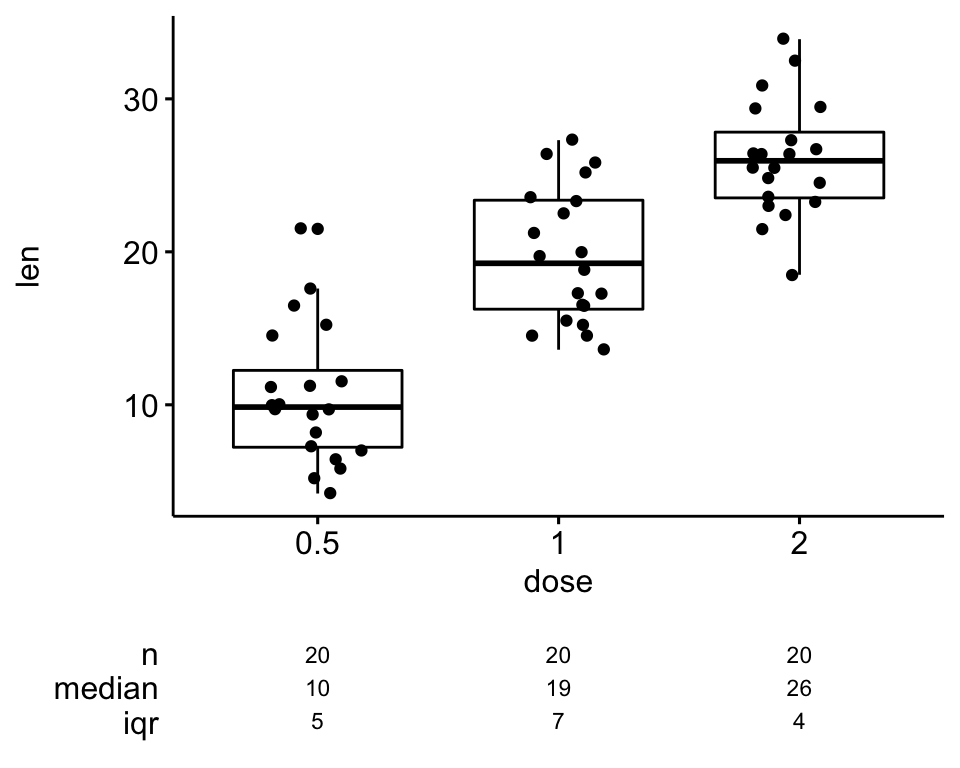



How To Create A Beautiful Plots In R With Summary Statistics Labels Datanovia




Boxplot Outliers Are Shown In Black Using Ggplotly Issue 1114 Plotly Plotly R Github



Coloring Plotly Box Plots Applying A Custom Color Scale To Plotly By Shah Newaz Khan Towards Data Science



How To Add Reference Lines To A Bar Plot In R How To In R



Ggplot2 Box Plot Quick Start Guide R Software And Data Visualization Easy Guides Wiki Sthda




R Ggplot Background Color Boxplot Stack Overflow



Data Visualization With Ggplot2



Control Ggplot2 Boxplot Colors The R Graph Gallery



Change Color Of Ggplot2 Boxplot In R 3 Examples Set Col Fill In Plot



Change Color Of Ggplot2 Boxplot In R 3 Examples Set Col Fill In Plot Manually Specify Colors Youtube



A Box And Whiskers Plot In The Style Of Tukey Geom Boxplot Ggplot2
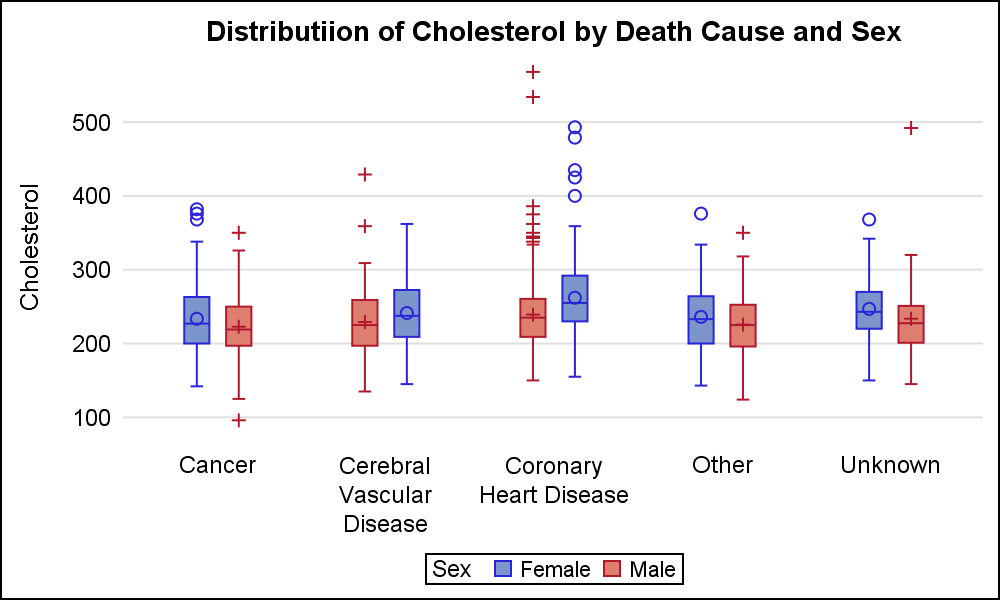



Box Plot Legend Graphically Speaking




R Boxplot To Create Box Plot With Numerous Examples




Creating Plots In R Using Ggplot2 Part 10 Boxplots




How To Color Box And Whisker Plot Yatomizonor
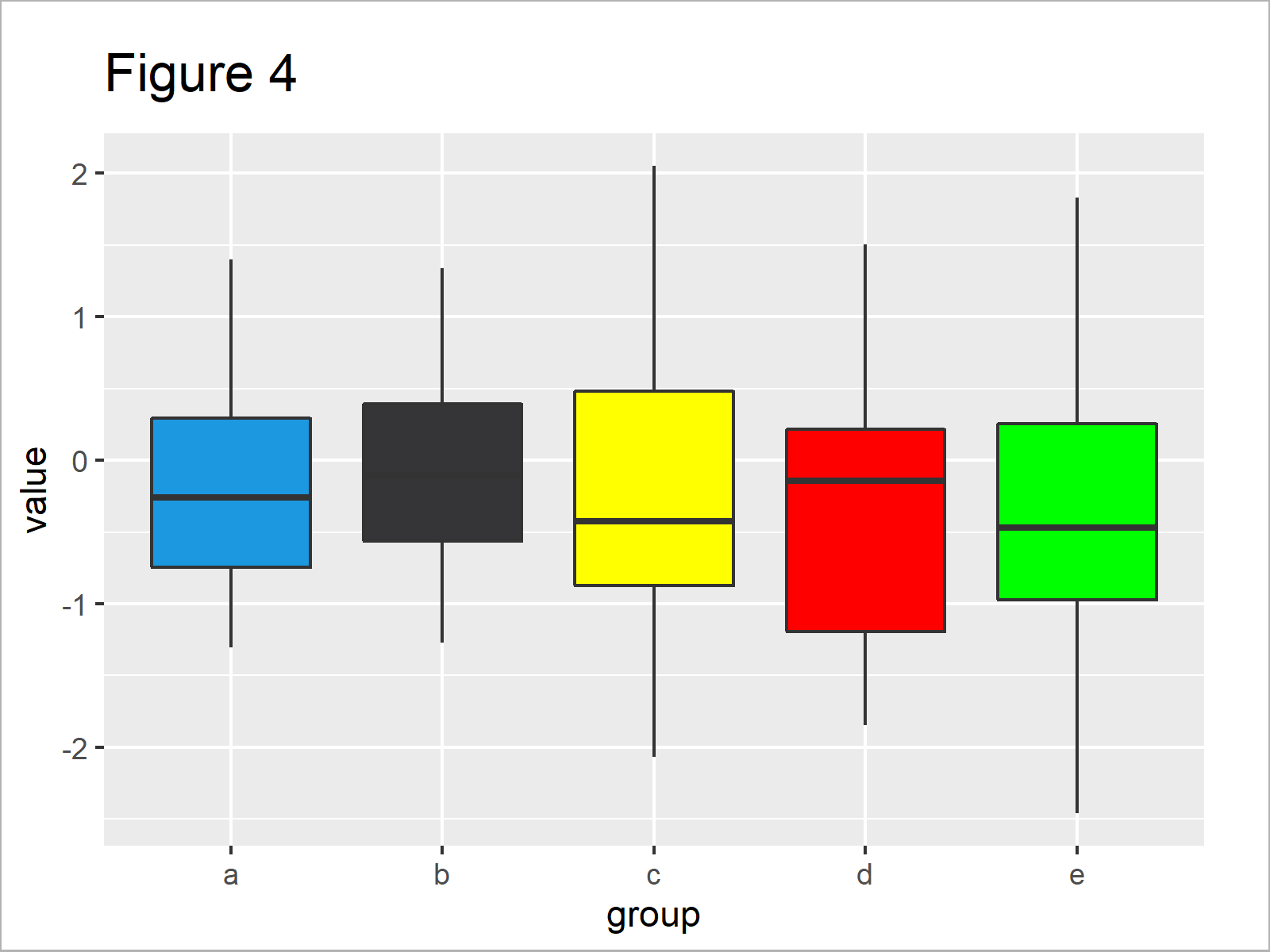



Change Color Of Ggplot2 Boxplot In R 3 Examples Set Col Fill In Plot




How To Draw Boxplot With Each Point And Background Color By R



1




How To Color Boxplots By A Variable In R With Ggplot2 Data Viz With Python And R




How To Make Grouped Boxplots With Ggplot2 Python And R Tips




Boxplot In R Boxplot By Group Multiple Box Plot



Side By Side Boxplots
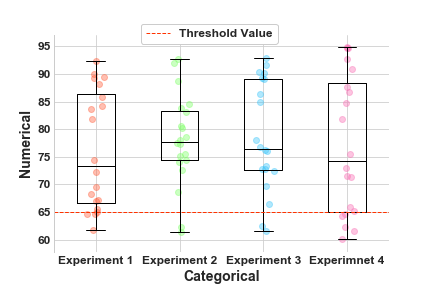



Scattered Boxplots Graphing Experimental Results With Matplotlib Seaborn And Pandas By Ciaran Cooney Towards Data Science




Boxplot How To Match Outliers Color To Fill Aesthetics Stack Overflow




How To Color Boxplots With R Colorbrewer Color Palettes Data Viz With Python And R
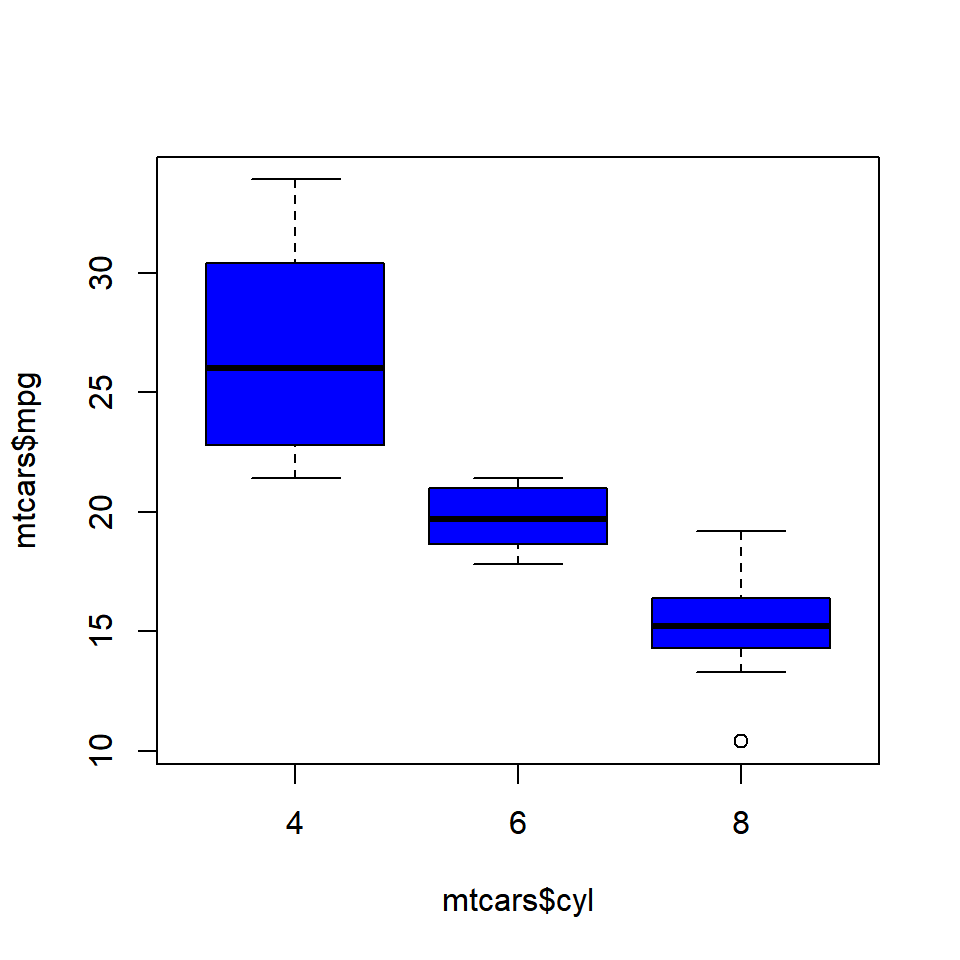



Data Visualization With R Box Plots Rsquared Academy Blog Explore Discover Learn



Ggplot2 Box Plot Quick Start Guide R Software And Data Visualization Easy Guides Wiki Sthda
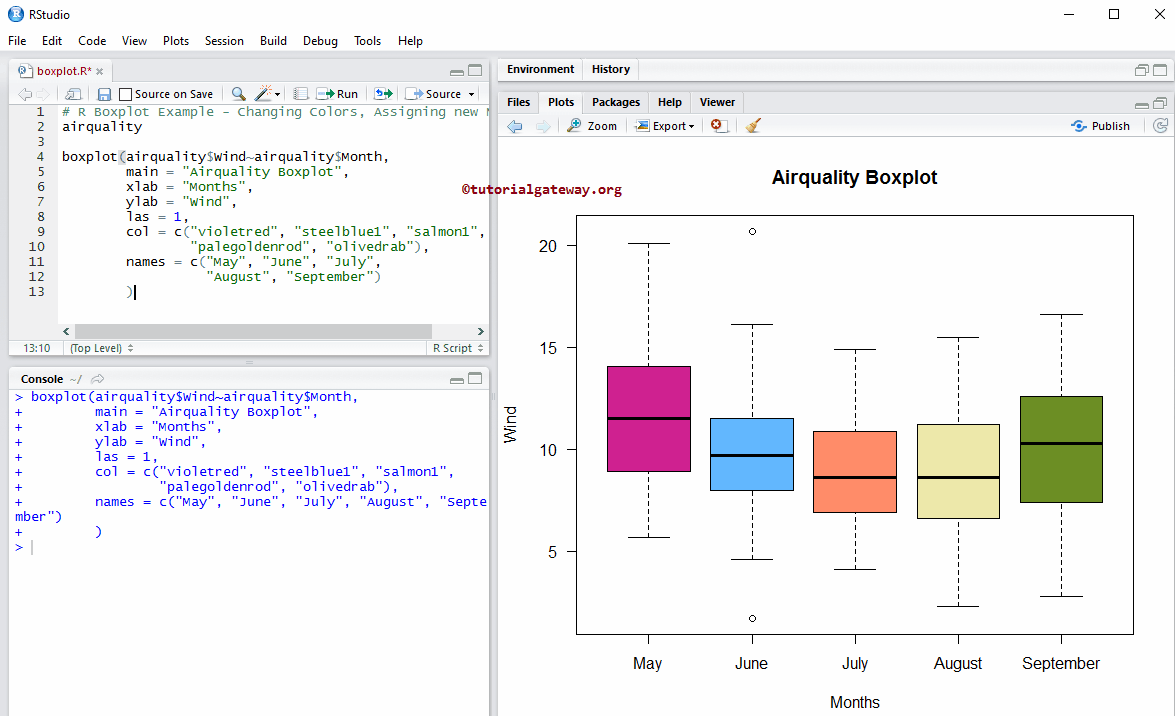



Boxplot In R Programming




Box Plot In R Using Ggplot2 Geeksforgeeks




Boxplot In R How To Make Boxplots Learn With Example
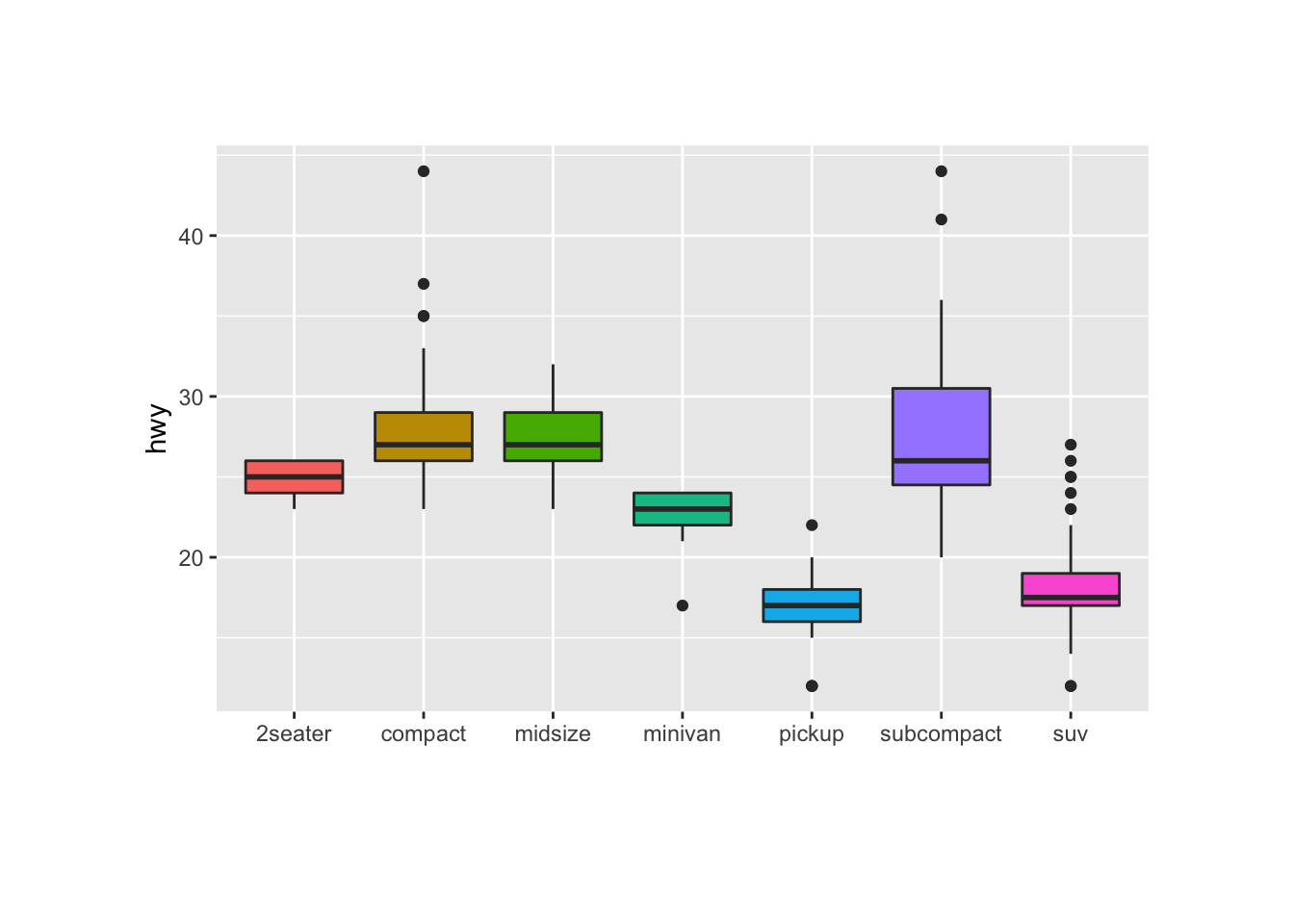



Control Ggplot2 Boxplot Colors The R Graph Gallery



1



Boxplot The R Graph Gallery



Exploring Ggplot2 Boxplots Defining Limits And Adjusting Style Water Data For The Nation Blog



A Box And Whiskers Plot In The Style Of Tukey Geom Boxplot Ggplot2




Boxplot In R How To Make Boxplots Learn With Example



Data Visualization In R Guide To Data Visualization In R
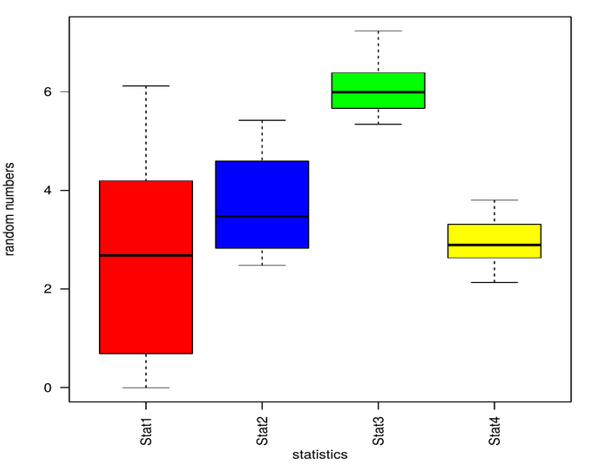



R Boxplot Labels How To Create Random Data Analyzing The Graph




Boxplot In R Boxplot By Group Multiple Box Plot




Colouring Different Group Data In Boxplot Using R Stack Overflow



Boxplots Ggplot Applied R Code
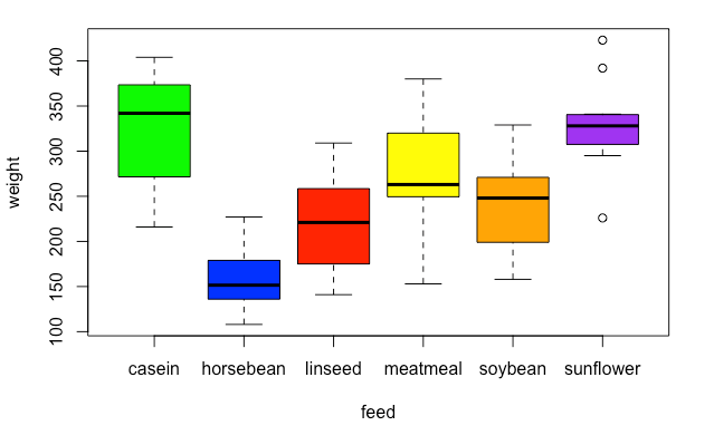



How To Make A Side By Side Boxplot In R Programmingr




R Box Whisker Plot Ggplot2 Learn By Example
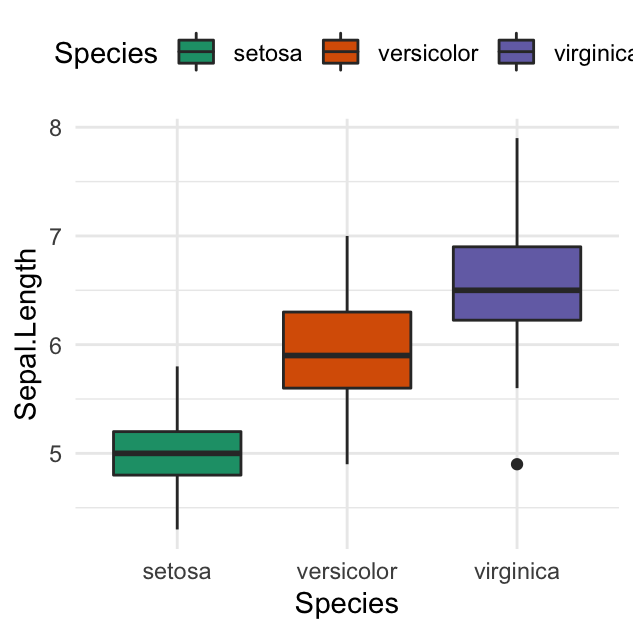



Ggplot Colors Best Tricks You Will Love Datanovia




How To Color Boxplots With R Colorbrewer Color Palettes Data Viz With Python And R




How To Manually Choose The Colors Of A Box Plot With Significance In Ggplot2 Stack Overflow




How To Color Boxplots By A Variable In R With Ggplot2 Data Viz With Python And R



Ggplot2 Box Plot Quick Start Guide R Software And Data Visualization Easy Guides Wiki Sthda




Box Plot Alternatives Beeswarm And Violin Plots Data Science Blog Understand Implement Succed




How To Color Boxplots By A Variable In R With Ggplot2 Data Viz With Python And R
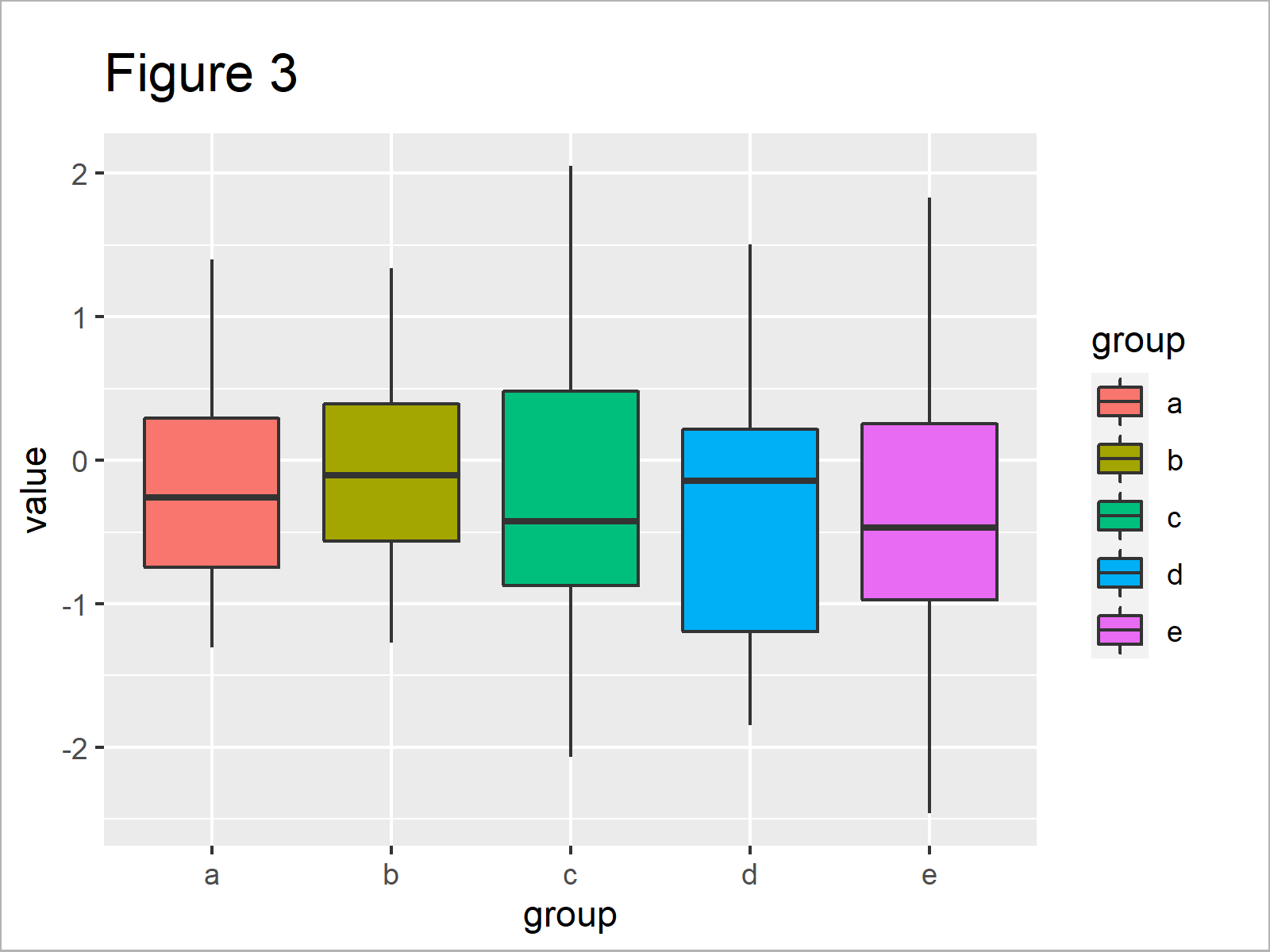



Change Color Of Ggplot2 Boxplot In R 3 Examples Set Col Fill In Plot




The Ultimate Guide To The Ggplot Boxplot Sharp Sight




Box Plots With Custom Fill Colors Matplotlib 3 4 3 Documentation
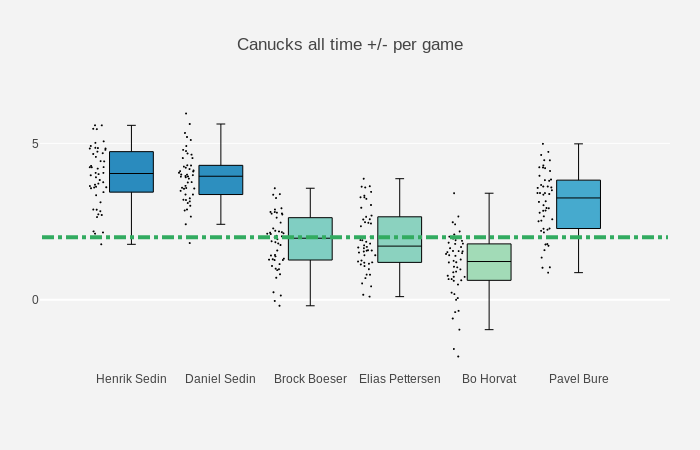



Coloring Plotly Box Plots Applying A Custom Color Scale To Plotly By Shah Newaz Khan Towards Data Science



2
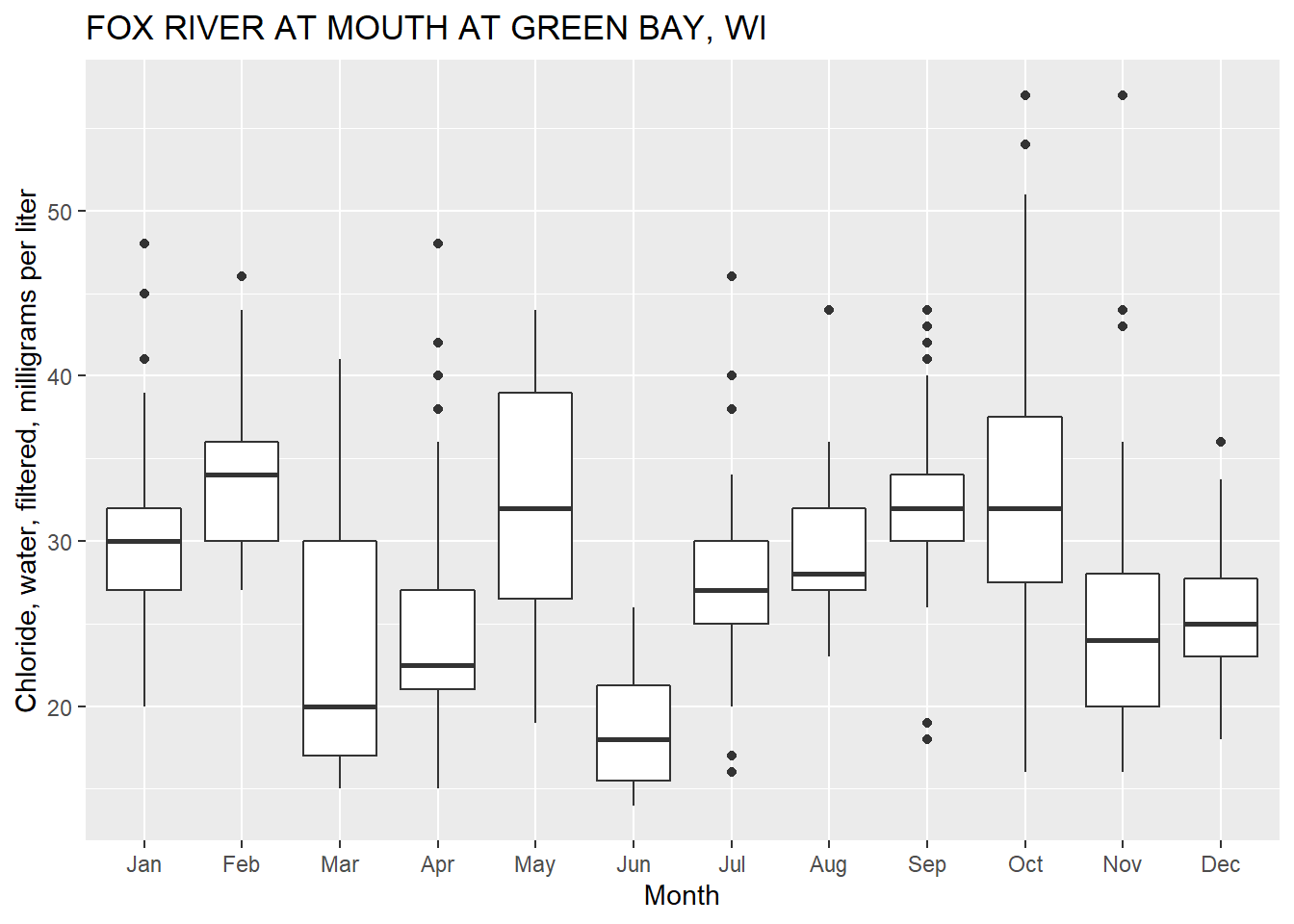



Exploring Ggplot2 Boxplots Defining Limits And Adjusting Style Water Data For The Nation Blog




Box Plot With Jittered Data Points In Ggplot2 R Charts



Ggplot2 Box Plot Quick Start Guide R Software And Data Visualization Easy Guides Wiki Sthda
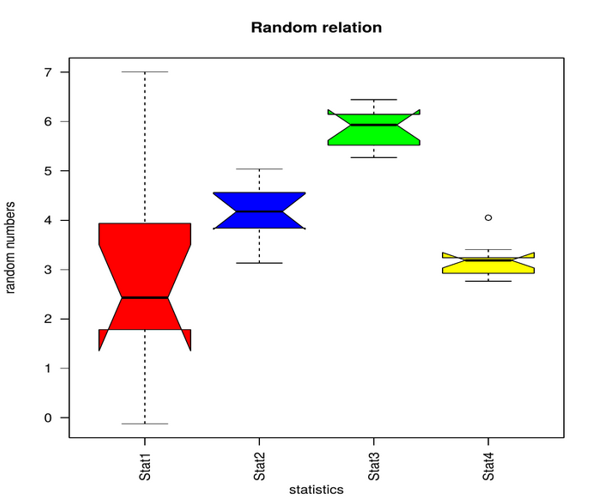



R Boxplot Labels How To Create Random Data Analyzing The Graph
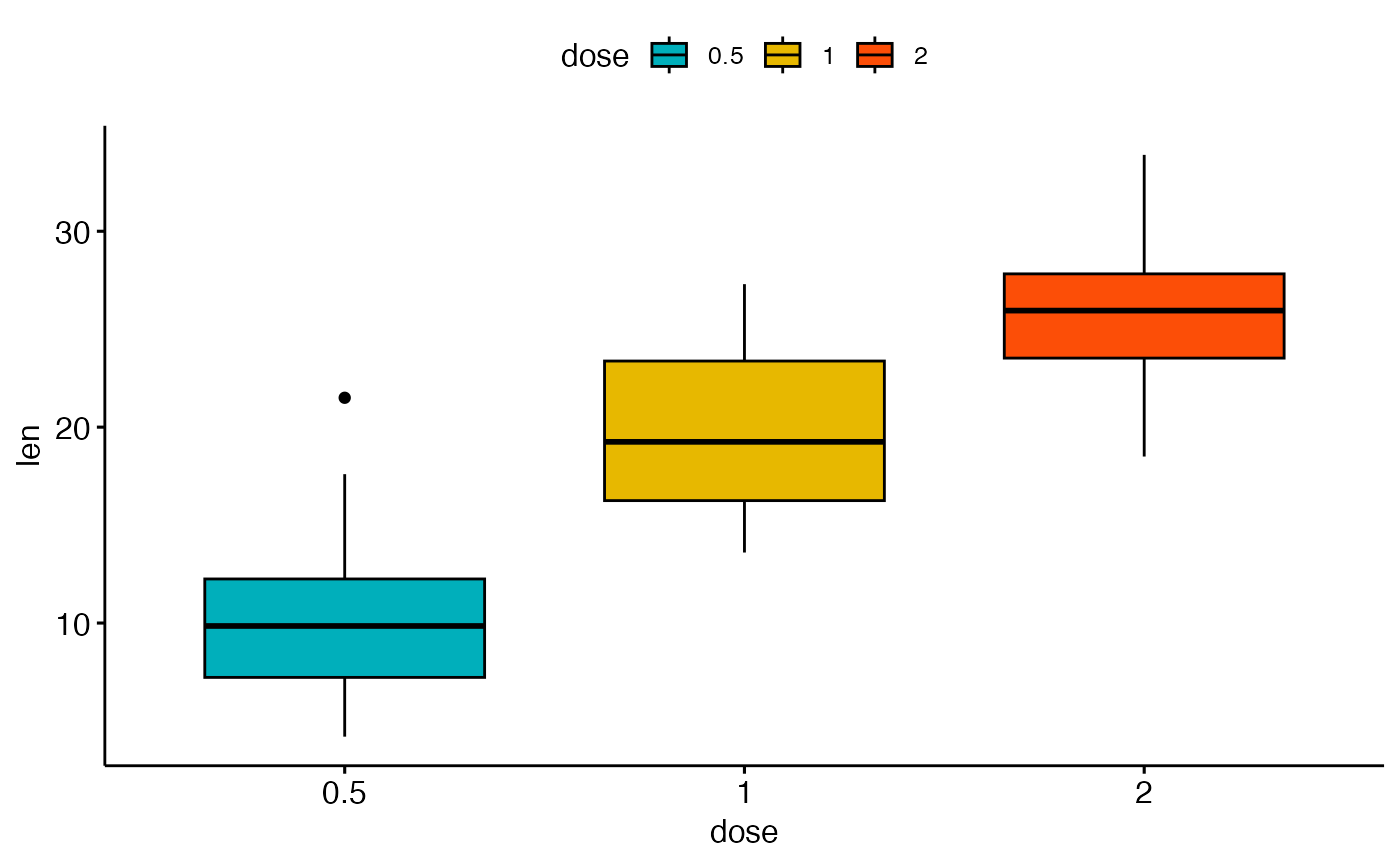



Box Plot Ggboxplot Ggpubr




Change Color Of Ggplot2 Boxplot In R Geeksforgeeks



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿